Posté le
6 reading time

In this article, we will explore the various aspects of absenteeism in the workplace. We will discuss the types of absenteeism, the underlying causes of this issue, as well as the consequences for businesses. We will also address the methodology for calculating the absenteeism rate and strategies for managing this reality in the professional environment. Finally, we will propose solutions to prevent and reduce absenteeism in the workplace.
What is absenteeism?
Work absenteeism refers to the frequent absence of a worker from their place of work. These absences can be justified or unjustified and are measured using HR management indicators.
Absenteeism in France, Belgium, and Luxembourg
Absenteeism in professional environments is a current topic, with significant variations in different countries.
In France, the absenteeism rate reached 6.7% in 2022, an increase compared to 2018, where it was 5.1%. This upward trend intensified in 2020 due to the global COVID-19 health crisis, resulting in an unprecedented peak of absenteeism. (Les Echos, 2023).
In Belgium, the trend is slightly different. In 2023, the rate decreased compared to the previous year, dropping from 3.61% to 3.24%. It is interesting to note that about one in three Belgians were never absent in 2023. (Mensura, 2024)
As for Luxembourg, the absenteeism rate stands at 5.2%. This is historically high compared to 2012, when it was 3.7%. (Fedil, s.d.)
Types of absenteeism
Absenteeism can manifest in various forms.
We present you with its most common forms:
- White absenteeism: it occurs when the worker is genuinely ill and unable to perform their work. They stay at home on medical advice to recover, thus avoiding spreading their germs and disrupting the smooth functioning of the company.
- Black absenteeism: unlike white absenteeism, this case occurs when the worker claims to be ill without a valid medical reason. The employee will stay at home for reasons other than illness.
- Gray absenteeism: this form is in a gray area, where the worker has medical issues, but the impact on their ability to work is uncertain. There can be tension between what the worker feels and their actual inability to work, often influenced by external factors such as work stress or personal problems.
- Pink absenteeism (or presenteeism): in this case, the worker is actually sick but chooses to go to work anyway. This can be motivated by fear of overburdening colleagues, fear of being seen in a negative light, or other similar reasons. However, this can lead to the spread of germs and an increased risk of additional absenteeism for the company, and even burnout for the worker.
These nuances of absenteeism underline the importance for businesses to understand the causes and adopt strategies to manage this reality in the workplace.
The causes of absenteeism
The causes of absenteeism in the workplace are varied and can be grouped into several categories.
These causes can be:
- Psychosocial: the high risk of burnout resulting from emotional stress, work intensity, stressful personal life, and job insecurity can lead to prolonged absences.
- Related to excessive workload: constant overwork, difficult working conditions, and a poor work environment can cause stress, tension, and fatigue. This can lead to absences due to physical and mental health reasons.
- Related to management style: an authoritarian and oppressive management style can create a climate of fear and stress among employees. This can promote absences due to mental health issues.
- Related to a loss of meaning at work: lack of connection with company values, inadequate communication, heavy processes, and tasks without added value can lead to decreased motivation and employee engagement, resulting in increased absenteeism.
It is crucial for companies to recognize these causes and adopt preventive measures. Identifying these causes helps reduce the risk of facing undesirable consequences that your company may encounter.
The consequences of absenteeism
The consequences of absenteeism manifest for both employees and businesses, as well as society as a whole.
Consequences for the employee
Absenteeism can have negative repercussions on the employee themselves. It can lead to a decrease in job satisfaction, difficulties in relationships with colleagues and supervisors, as well as financial problems.
Frequent absences can result in demotivation and frustration for the employee, due to personal or health issues preventing them from regularly attending work. This can also undermine self-confidence and self-esteem, contributing to professional discomfort.
Moreover, absenteeism can compromise the employee’s professional relationships. By regularly being away from the workplace, they risk losing contact with their colleagues and supervisors. This can lead to a deterioration of relationships within the team.
Finally, financially, repeated absences can result in a loss of salary. In the most serious cases, disciplinary sanctions such as salary reduction or dismissal are also possible.
Consequences for the company
For a company, absenteeism results in decreased productivity, additional costs related to replacing absent employees, increased workload for other employees, and a decline in the quality of customer service.
Absenteeism disrupts the distribution of tasks within the team. This can lead to an overload of work and overall inefficiency. The additional costs associated with replacing absent staff can heavily impact the company’s finances, especially if absenteeism is recurrent.
Moreover, absenteeism can harm the quality of customer service, particularly if absent employees hold key positions within the company. This can have a negative impact on the company’s reputation and customer loyalty.
Consequences for society
At the societal level, absenteeism has an economic impact, affects the quality of public services, and can compromise social cohesion.
Economically, absenteeism can hinder economic growth due to decreased production and consumption. The costs associated with absenteeism can also have repercussions on public finances.
In public services, absenteeism can compromise the quality of services provided to the population. For example, frequent absences in the healthcare sector can lead to delays in medical care.
Finally, on a social level, absenteeism can cause tensions within society. It can fuel a sense of injustice and discontent among employees and undermine solidarity within work teams.
Calculating the absenteeism rate
Absenteeism is quantifiable and is measured using a formula to estimate the absenteeism rate.
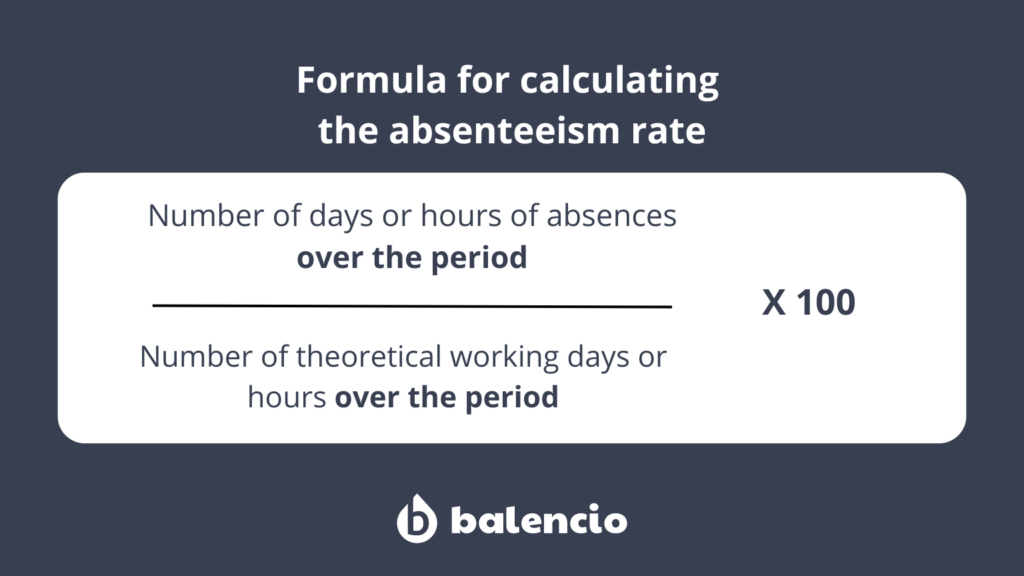
To calculate the absenteeism rate in a company, a specific formula is used.
This formula compares the number of observed days or hours of absence over a given period with the number of theoretical days or hours of work scheduled for the same period.
To obtain the absenteeism rate, you divide the total number of absences (in days or hours) by the total number of theoretical days or hours of work for the period under consideration.
The result of this division is then multiplied by 100 to express the rate as a percentage. This absenteeism rate reflects the proportion of work time not fulfilled due to absences.
Typically, the periods chosen for this calculation are the month and the year. However, it can be calculated on a weekly, monthly, quarterly, or yearly basis.
Managing absenteeism in a company
To manage absenteeism in a company, it is essential to implement effective measures.
First and foremost, clear policies regarding absences need to be established, including notification procedures and consequences for abuse.
Next, it’s important to closely monitor absences by maintaining accurate records to identify recurring patterns and reasons for absence. Managers need to be trained to recognize and manage absences constructively, ensuring open dialogue with the affected employees.
Finally, it is crucial to promote a healthy work environment by offering wellness programs and fostering communication and collaboration within the team.
Which solutions to prevent absenteeism
To prevent absenteeism in the workplace, there are several effective solutions to implement.
First and foremost, it is essential to promote a healthy and balanced work environment by offering health and wellness programs, as well as initiatives for stress management and conflict resolution.
Next, offering flexible schedules and telecommuting options can help employees better balance their professional and personal obligations, thereby reducing absenteeism reasons.
Furthermore, recognizing and valuing employees’ work, as well as providing them with professional development opportunities, can enhance their engagement and motivation, thereby reducing the risks of unjustified absences.
Finally, maintaining open and transparent communication with employees, consulting them on decisions that affect them, and involving them in the life of the company can help strengthen their sense of belonging and reduce absenteeism rates.
Balencio, your ally against absenteeism
Balencio offers you a digital platform to collect feedback from your staff. With the Balencio dashboard, you can provide HR departments and executive committees with reliable digital data on the causes of absenteeism within your organization. Our filtering system allows you to identify specific issues related to each department, team, or job category. Once the solutions are identified, you can implement a viable action plan for sustainable improvement.
Thanks to our 360-degree approach, you can proactively address issues with your employees in a constructive and interactive manner. The implementation of an action plan over a defined period is essential to reduce the number of absences, whether short or long-term. The indicators integrated into our modules help you target your strategies and find sustainable solutions.
Table of content
Balencio’s HR news directly in your inbox
{Newsletter form}